perpendicular
collision
coma
Comets vaporize and break up after they have passed close to the Sun many times. The small pieces from the comet’s nucleus spread out into a loose group within the original orbit of the comet. These pieces of dust and rock, along with those derived from other sources, are called meteoroids. A meteoroid that burns up in Earth’s atmosphere is called a meteor.
Each time Earth passes through the loose group of particles within the old orbit of a comet, many small particles of rock and dust enter the atmosphere. Because more meteors than usual are seen, the event is called a meteor shower. When a meteoroid is large enough, it might not burn up completely in the atmosphere. If it strikes Earth, it is called a meteorite. Most meteorites are probably debris from asteroid collisions or broken-up comets, but some originate from the Moon and Mars.
porch
culprit
fussing
Ancient Greeks, Romans, and other early cultures observed patterns of stars in the night sky called constellations. They imagined that the constellations represented mythological characters, animals, or familiar objects.
Modern astronomy divides the sky into 88 constellations, many of which were named by early astronomers.
When you refer to the brightness of a star, you can refer to its absolute magnitude or its apparent magnitude. The absolute magnitude of a star is a measure of the amount of light it gives off. A measure of the amount of light received on Earth is the apparent magnitude.
luxes
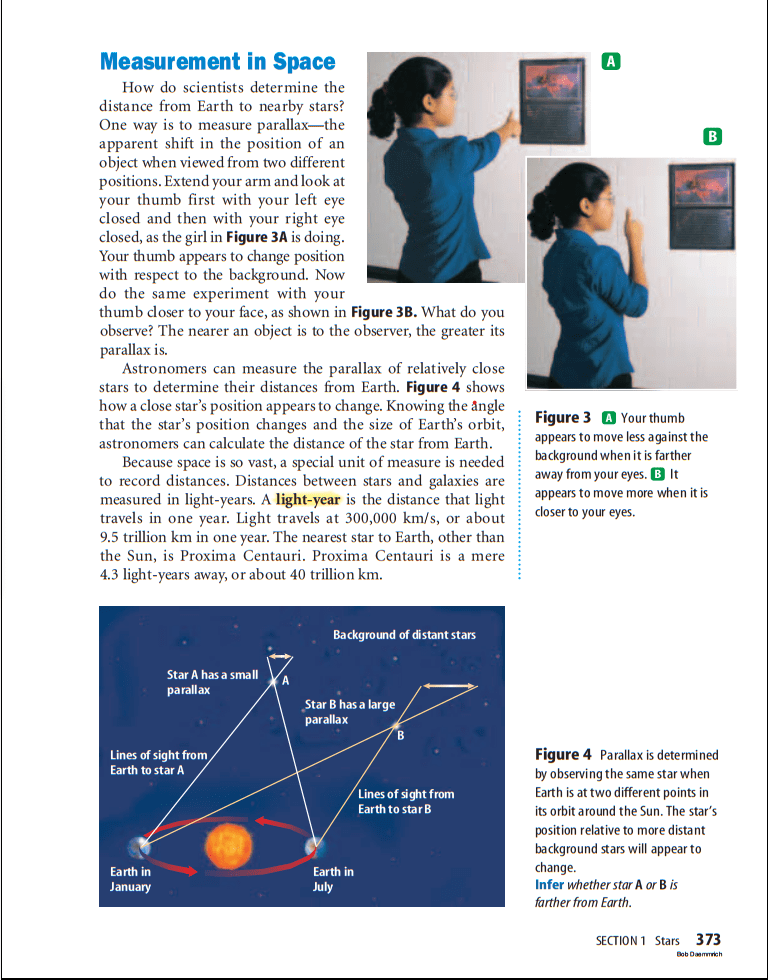
A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year. Light travels at 300,000 km/s, or about 9.5 trillion km in one year.


diffraction
grating
spectra
Astronomers study the composition of stars by observing their spectra. When fitted into a telescope, a spectroscope acts like a prism. It spreads light out in the rainbow band called a spectrum.
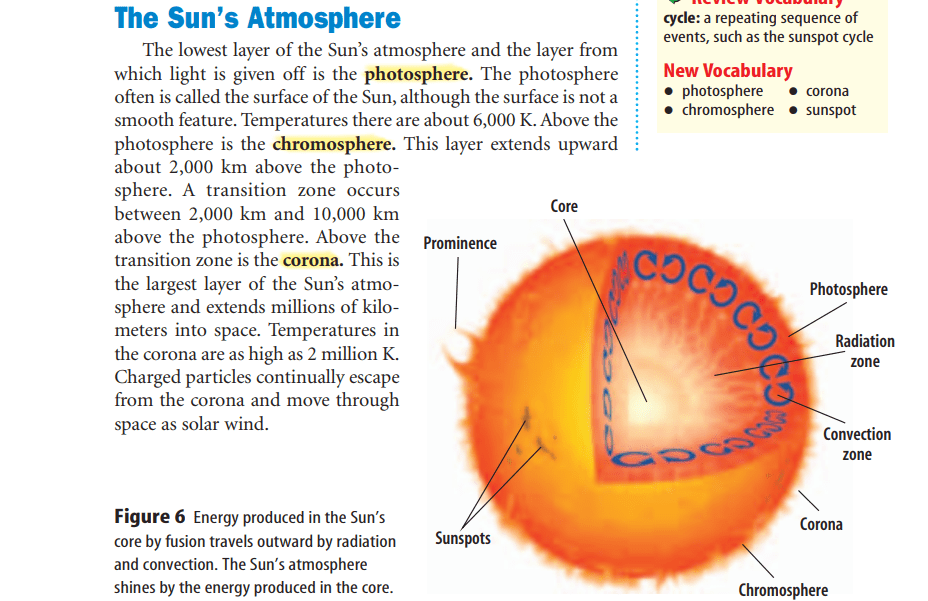
radiation zone
convection zone
Areas of the Sun’s surface that appear dark because they are cooler than surrounding areas are called sunspots.
Times when many large sunspots occur are called sunspot maximums. Sunspot maximums occur about every 10 to 11 years. Periods of sunspot minimum occur in between.
Sunspots are related to several features on the Sun’s surface. The intense magnetic fields associated with sunspots might cause prominences, which are huge, arching columns of gas
Gases near a sunspot sometimes brighten suddenly, shooting outward at high speed. These violent eruptions are called solar flares.
Coronal mass ejections (CMEs) occur when large amounts of electrically-charged gas are ejected suddenly from the Sun’s corona. CMEs can occur as often as two or three times each day during a sunspot maximum.
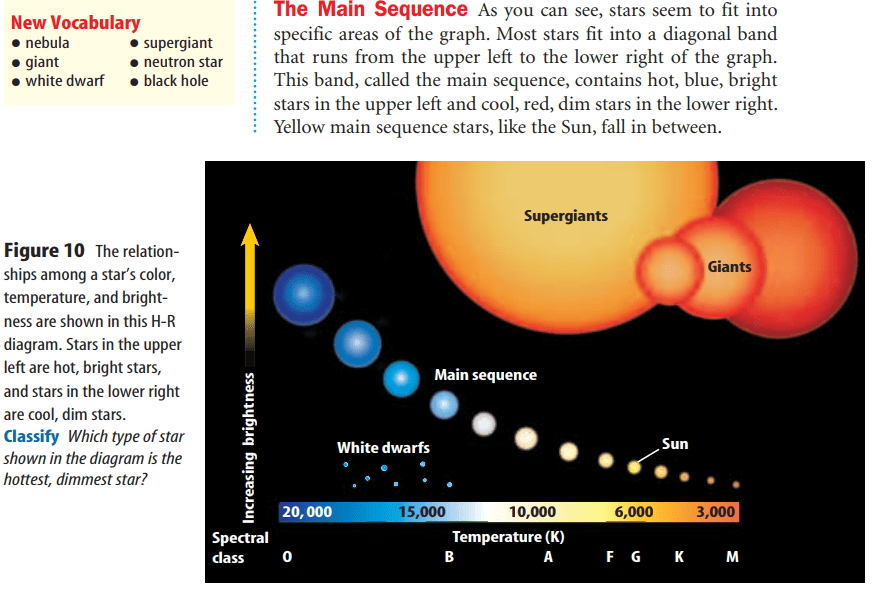
Stars also can move through space as a cluster. In a star cluster, many stars are relatively close, so the gravitational attraction among the stars is strong. Most star clusters are far from the solar system.
Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a nebula.
tripod
emit
deplete
exert
vacuum cleaner
condense
A galaxy is a large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. Earth and the solar system are in a galaxy called the Milky Way.
The Large Magellanic Cloud is an irregular galaxy.
A second idea is called the oscillating model. In this model, the universe began with expansion. Over time, the expansion slowed and the universe contracted. Then the process began again, oscillating back and forth. Some scientists still hypothesize that the universe expands and contracts in a cycle.
A third model of how the universe formed is called the big bang theory. The universe started with a big bang and has been expanding ever since. This theory will be described later.
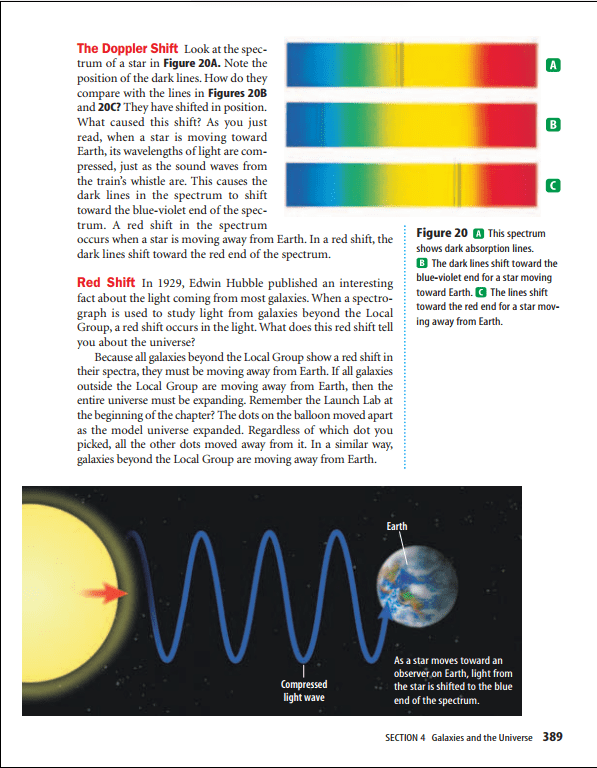
The whistle has a higher pitch as the train approaches you. Then the whistle seems to drop in pitch as the train moves away. This effect is called the Doppler shift.
opaque
parallax
Unit 5
charcoal
hoist
stencil
bombard
cram
fluorescent
unconventional
An electrode is a piece of metal that can conduct electricity. One electrode, called the anode, has a positive charge. The other, called the cathode, has a negative charge.
Crookes’s tube is known as a cathode-ray tube, or CRT. They were used for TV and computer monitors for many years.
A proton is a positively charged particle present in the nucleus of all atoms. The rest of each atom is empty space occupied by the atom’s almost massless electrons.
Electrons travel in a region surrounding the nucleus, which is called the electron cloud.
The
Atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. The smallest of the atoms, the hydrogen atom, has one proton in its nucleus, so hydrogen’s atomic number is 1.
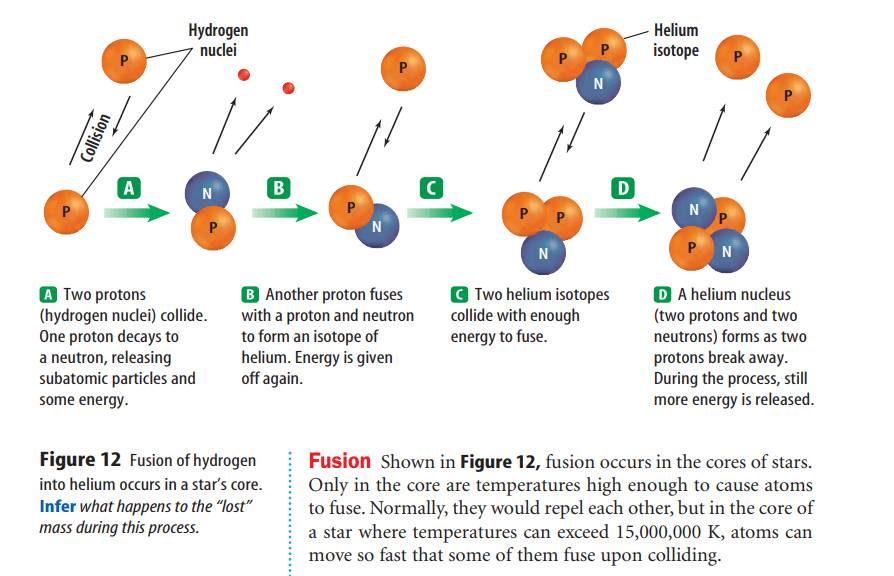

Isotopes (I suh tohps) are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.
The release of nuclear particles and energy is called radioactive decay. When the particles that are ejected from a nucleus include protons, the atomic number of the nucleus changes. When this happens, one element changes into another. The changing of one element into another through radioactive decay is called transmutation.
Together, the energy and particles are called nuclear radiation. An alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons.
repulsion
veer off: to begin to go in the wrong direction.
The rate of decay of a nucleus is measured by its half-life. The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the amount of time it takes for half of a sample of the element to decay.
Alpha and beta particles, for example, are accelerated in particle accelerators to speeds fast enough that they can smash into a large nucleus and be absorbed on impact. The absorbed particle converts the target element into another element with a higher atomic number. The new element is called a synthetic element because it is made by humans.
The process of artificial transmutation has been adapted so that radioactive isotopes of normally stable elements can be used in hospitals and clinics using specially designed equipment.These isotopes, called
tracer elements, are used to diagnose disease and to study environmental conditions. The radioactive isotope is introduced into a living system such as a person, animal, or plant. It then is followed by a device that detects radiation while it decays.
penetrate
periodic event
In the modern periodic table on the next page, the elements still are organized by increasing atomic number. The rows or periods are labeled 1–7. A period is a row of elements in the periodic table whose properties change gradually and predictably. The periodic table has 18 columns of elements. Each column contains a group, or family, of elements. A group contains elements that have similar physical or chemical properties.
metalloids
synthetically
A
metal is an element that has luster, is a good conductor of heat and electricity, is malleable, and is ductile. The ability to reflect light is a property of metals called luster. Many metals can be pressed or pounded into thin sheets or shaped into objects because they are malleable (MAL yuh bul). Metals are also ductile (DUK tul), which means that they can be drawn out into wires.
Nonmetals are usually gases or brittle solids at room temperature and poor conductors of heat
and electricity. There are only 17 nonmetals, but they include many elements that are essential for life carbon, sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and iodine. a metalloid is an element that shares some properties with metals and some with nonmetals. These elements also are called semimetals.
luster
graphite
pewter
Elements often combine with oxygen to form oxides and chlorine to form chlorides. For example, two hydrogen atoms combine with one oxygen atom to form oxide, H2O or water. One sodium atom combines with one chlorine atom to form sodium chloride, NaCl or table salt. The location of an element on the periodic table is an indication of how it combines with other elements.
A semiconductor doesn’t conduct electricity as well as a metal, but does conduct electricity better than a nonmetal.
Ammonia
disinfectant
detergents
forensic
halogens: salt-former
blimps
filament: a slender threadlike object or fiber, especially one found in animal or plant structures; a conducting wire or thread with a high melting point, forming part of an electric bulb or vacuum tube and heated or made incandescent by an electric current.
A strobe light is a type of specialized lamp that produces a continuous series of short, bright flashes of light,
ores: Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.
hemoglobin
A catalyst is a substance that can make something happen faster but is not changed itself.
There are two series of inner transition elements. The first
series, from cerium to lutetium, is called the lanthanides. The
lanthanides also are called the rare earths because at one time
they were thought to be scarce. The lanthanides are usually
found combined with oxygen in Earth’s crust. The second series
of elements, from thorium to lawrencium, is called the actinides.
misch metal
actinides
Amalgam
resin: any natural or synthetic organic compound consisting of a noncrystalline or viscous liquid substance.
Orthodontists: is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, and misaligned bite patterns.
gourd
a strand of
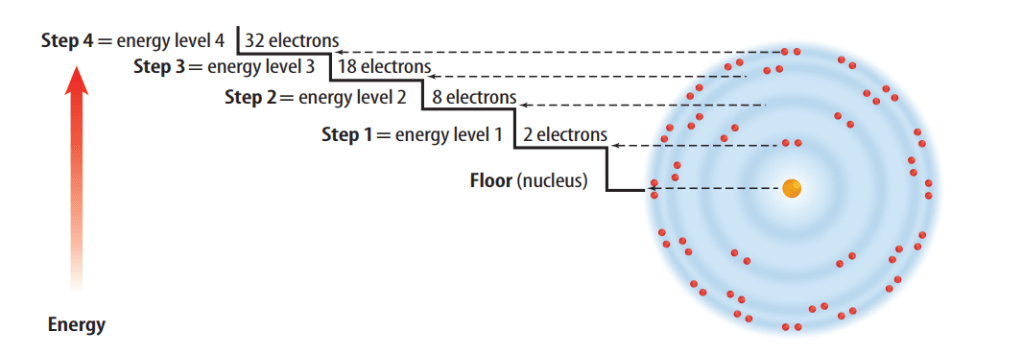
Although all the electrons in an atom are somewhere in the electron cloud, some electrons are closer to the nucleus than others. The different areas for an electron in an atom are called energy levels. Each level represents a different amount of energy.
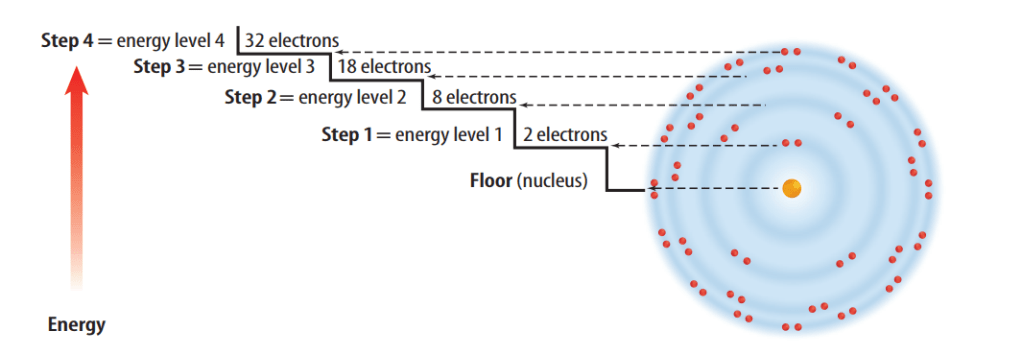
It is handy to have an easier way to represent the atoms and the electrons in their outer energy levels. You can do this with electron dot diagrams.An electron dot diagram is the symbol for the element surrounded by as many dots as there are electrons in its outer energy level.
A chemical bond is the force that holds two atoms together. Chemical bonds unite atoms in a compound much as glue unites the pieces of the model in.
resemble
Atoms form bonds with other atoms using the electrons in their outer energy levels. They have four ways to do this—by losing electrons, by gaining electrons, by pooling electrons, or by sharing electrons with another element.
ion, any atom or group of atoms that bears one or more positive or negative electrical charges.
Gains and Losses
When ions dissolve in water, they separate. Because of their positive and negative charges, the ions can conduct an electric current. If wires are placed in such a solution and the ends of the wires are connected to a battery, the positive ions move toward the negative terminal and the negative ions move toward the positive terminal. This flow of ions completes the circuit.
A sodium ion is represented by the symbol Na+ and a chloride ion is represented by the symbol Cl-.
The positive sodium ion and the negative chloride ion are strongly attracted to each other. This attraction,
which holds the ions close together, is a type of chemical bond called an ionic bond. A compound is a pure substance containing two or more elements that are chemically bonded.
Pooling
Metals can form bonds with other metal atoms, but in a different way. In a metal, the electrons in the
outer energy levels of the atoms are not held tightly to individual atoms. Instead, they move freely among all the ions in the metal, forming a shared pool of electrons, as shown in Figure 15. Metallic bonds form when metal atoms share their pooled electrons. This bonding affects the properties of metals. For example, when a metal is hammered into sheets or drawn into a wire, it does not break. Instead, layers of atoms slide over one another. The pooled electrons tend to hold the atoms together. Metallic bonding also is the reason that metals conduct electricity well. The outer electrons in metal atoms readily move from one atom to the next to transmit current.
Sharing
Atoms of many elements become more stable by sharing electrons. The chemical bond that forms
between nonmetal atoms when they share electrons is called a covalent (koh VAY luhnt) bond. Shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms. They move back and forth between the outer energy levels of each atom in the covalent bond. So, each atom has a stable outer energy level some of the time. Covalently bonded compounds are called molecular compounds.
The atoms in a covalent bond form a neutral particle, which contains the same numbers of positive and negative charges. The neutral particle formed when atoms share electrons is called a molecule. A molecule is the basic unit of a molecular compound.
A polar bond is a bond in which electrons are shared unevenly. The bonds between the oxygen atom and hydrogen atoms in the water molecule are another example of polar bonds.
Molecules that do not have these uneven charges are called nonpolar molecules. Because each element differs slightly in its ability to attract electrons, the only completely nonpolar bonds are bonds between atoms of the same element. One example of a nonpolar bond is the triple bond in the nitrogen molecule.
Like ionic compounds, some molecular compounds can form crystals, in which the basic unit is a molecule. Often you can see the pattern of the units in the shape of ionic and molecular crystals.
Compounds can be described using element symbols and numbers. For example, The resulting hydrogen molecule is represented by the symbol H2. The small 2 after the H in the formula is called a subscript.
Sub means “below” and script means “write,” so a subscript is a number that is written a little below a line of text. The subscript 2 means that two atoms of hydrogen are in the molecule.

A chemical formula is a combination of chemical symbols and numbers that shows which elements are present in a compound and how many atoms of each element are present. When no subscript is shown, the number of atoms is understood to be one.

covalent compound: the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms.
A process that produces chemical change is a chemical reaction.
The substances that react are called the reactants.
Reactants are the substances that exist before the reaction begins. The substances that form as a result of the reaction are called the products.
Baking soda is the compound sodium hydrogen carbonate (often called sodium bicarbonate).
vigorous
acetic acid
Chemists try to find out which reactants are used and which products are formed in a chemical reaction. Then, they can write it in a shorthand form called a chemical equation. A chemical equation tells chemists at a glance the reactants, products, and proportions of each substance present. Some equations also tell the physical state of each substance.
According to the law of conservation of mass, the mass of the products must be the same as the mass of the reactants in that chemical reaction. This principle was first stated by the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794), who is considered the first modern chemist.
When balancing chemical equations,numbers are placed before the formulas as you did for Ag. These are called coefficients.
welding torch
Methane
turn off the ignition
Where does this energy come from? To answer this question, think about the chemical bonds that break
and form when atoms gain, lose, or share electrons. When such a reaction takes place, bonds break in the reactants and new bonds form in the products. In reactions that release energy, the products are more stable, and their bonds have less energy than those of the reactants. The extra energy is released in various forms—light, sound, and thermal energy.
Reactions can release or absorb several kinds of energy, including electricity, light, sound, and thermal energy. When thermal energy is gained or lost in reactions, special terms are used. Endothermic (en doh THUR mihk) reactions absorb thermal energy. Exothermic (ek soh THUR mihk) reactions release thermal energy. The root word therm refers to heat, as it does in thermos bottles and thermometers.
To start any chemical reaction, a minimum amount of energy is needed.
This energy is called the activation energy of the reaction.
The rate of reaction tells how fast a reaction occurs after it has started.
The amount of substance present in a certain volume is called the concentration of that substance. If you increase the concentration, you increase the number of particles of a substance per unit of volume.
A substance that slows down a chemical reaction is called an inhibitor.
butylated hydroxytoluene
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction. Catalysts do not appear in chemical equations, because they are not changed permanently or used up.
combustion
proteases
impervious

Leave a comment