Unit 6
ballast
deadweight
cobblestone
pollen
sprint
reference point
Displacement includes the distance between the starting and ending points and the direction in which you travel.
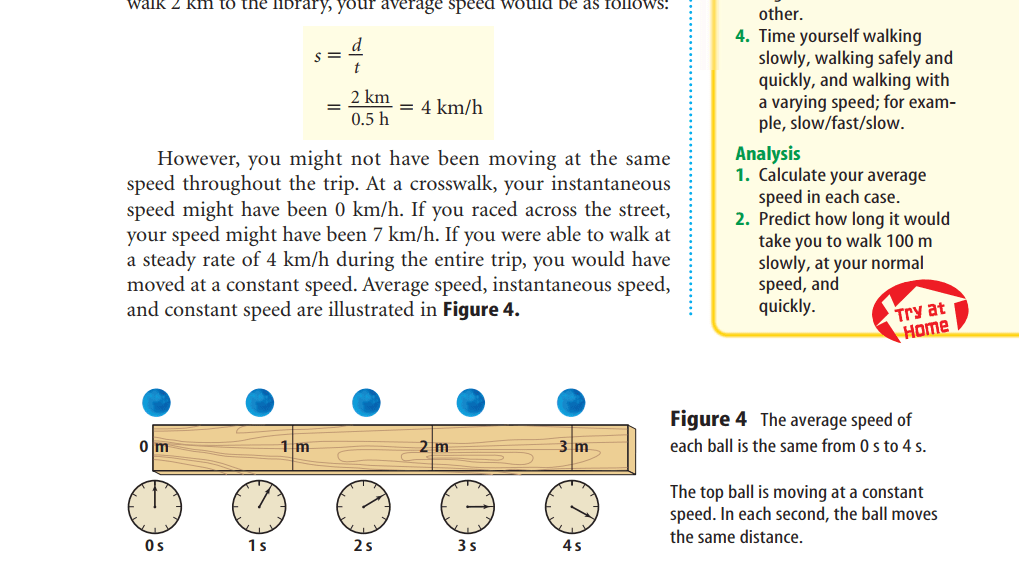
Average speed is found by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken.
The speed of an object at one instant of time is the object’s instantaneous speed.
constant speed
The direction of an object’s motion can be described with its velocity. The velocity of an object is the speed of the object and the direction of its motion.
intersection
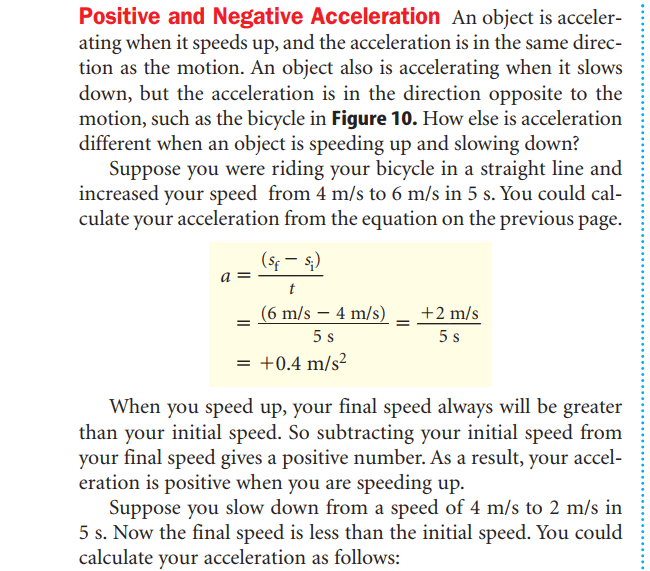
Acceleration is the change in velocity divided by the time it takes for the change to occur.
the final speed & the initial speed
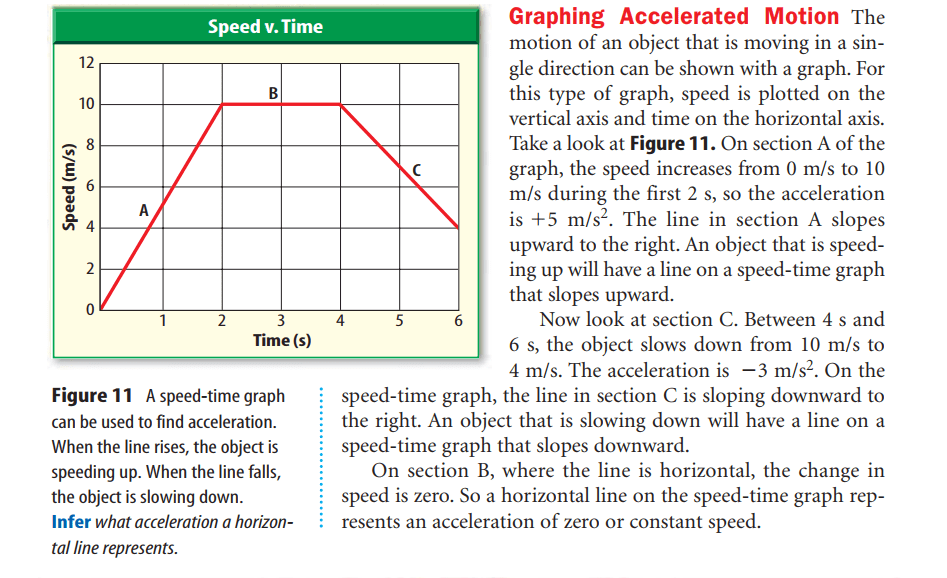
speed is plotted on the vertical axis and time on the horizontal axis.
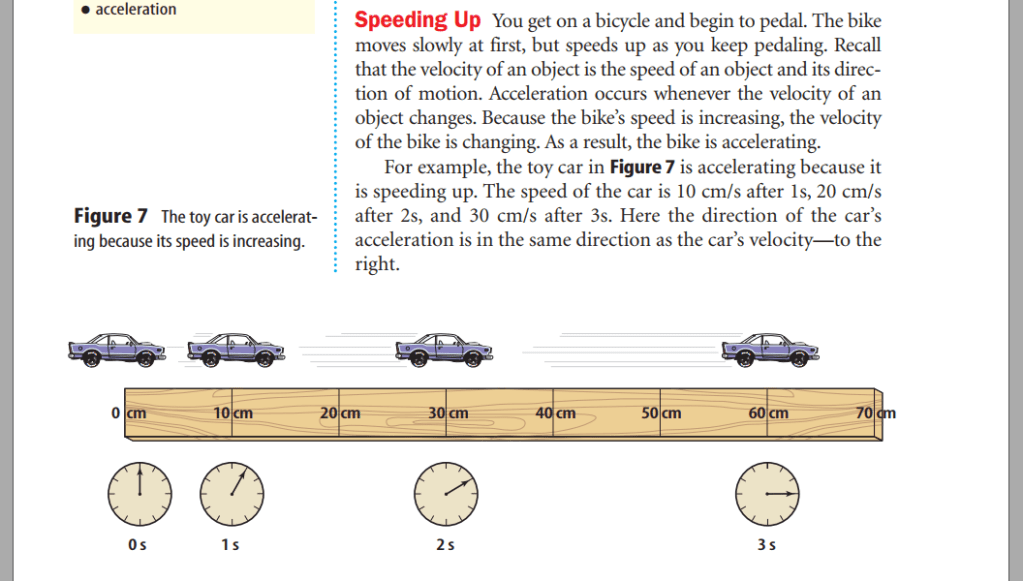
collision
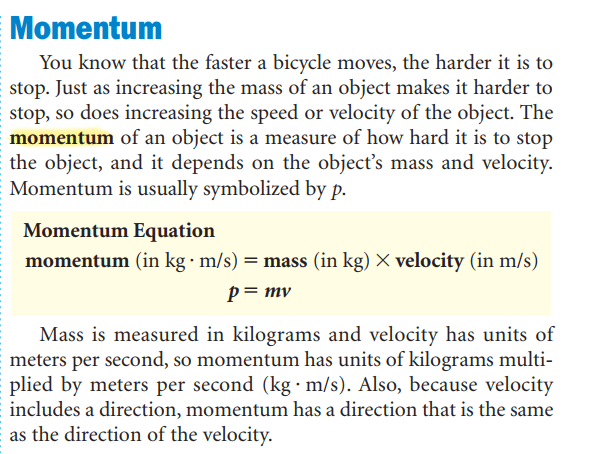
Mass is the amount of matter in an obeject.
A big racquet rather than a small paddle is used to change its motion.
The tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion is called inertia. The amount of resistance to a change in motion increases as an object’s mass increases.
The law of conservation of momentum means that collisions between these objects don’t change the total momentum of all the objects in the group.
insulated foam meat trays
A force is a push or a pull.
A force can be exerted in different ways.
The combination of all the forces acting on an object is the net force.
Two or more forces exerted on an object are balanced forces if their effects cancel each other and they do not change the object’s velocity. If the forces on an object are balanced, the net force is zero. If the net force is not zero, the forces are unbalanced forces. Then the effects of the forces don’t cancel, and the object’s velocity changes.
Newton’s first law of motion describes how an object moves when the net force acting on it is zero.
According to Newton’s first law of motion, if the net force acting on an object is zero, the object remains at rest, or if the object is already moving, continues to move in a straight line with constant speed.
The force that brings nearly everything to a stop is friction, which is the force that acts to resist sliding between two touching surfaces.
The type of friction that prevents an object from moving when a force is applied is called static friction. Static friction is caused by the attraction between the atoms on the two surfaces that are in contact. This causes the surfaces to stick or weld together where they are in contact. Usually, as the surface gets rougher and the object gets heavier, the force of static friction will be larger. To move the object, you have to exert a force large enough to break the bonds holding two surfaces together.
Sliding friction is due to the microscopic roughness of two openers, as shown in Figure 5. The surfaces tend to stick together where they touch. The bonds between the surfaces are broken and form again as the surfaces slide past each other. This causes sliding friction.
Rolling friction occurs when an object rolls across a surface.

The force of gravity exists between any two objects that have mass. Gravity always is attractive and pulls objects toward each other. A gravitational attraction exists between you and every object in the universe that has mass. However, the force of gravity depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. The gravitational force becomes weaker the farther apart the objects are and also decreases as the masses of the objects involved decrease.
In 1687, Newton published a book that included the law of universal gravitation.
circular motion
When an object moves in circular motion, the net force on the object is called centripetal force. The direction of the centripetal force is toward the center of the object’s circular path.
Air resistance is a form of friction that acts to slow down any object moving in the air. Air resistance is a force that gets larger as an object moves faster. Air resistance also depends on the shape of an object.A piece of paper crumpled into a ball falls faster than a flat piece of paper falls.
When the air resistance force equals the weight, the net force on the object is zero. By Newton’s second law, the object’s acceleration then is zero, and its speed no longer increases. When air resistance balances the force of gravity, the object falls at a constant speed called the terminal velocity.
The center of mass is the point in an object that moves as if all the object’s mass were concentrated at that point.
The forces exerted by two objects on each other are often called an action-reaction force pair. You might think that because action-reaction forces are equal and opposite that they cancel. However, action and reaction force pairs don’t cancel because they act on different objects. Forces can cancel only if they act on the same object.
propel
Air bags have saved more than a thousand lives since 1992. They are like having a giant popcorn kernel in the dashboard that pops and becomes many times its original size. But unlike popcorn, an air bag is triggered by impact, not temperature.
buckled your seat belt
steering wheel
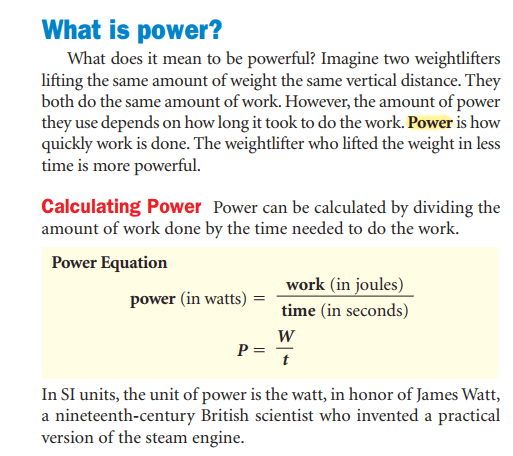
Work is done when a force causes an object to move in the same direction that the force is applied.
kinetic energy
potential energy
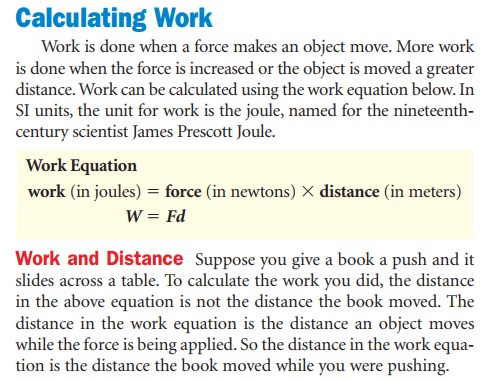
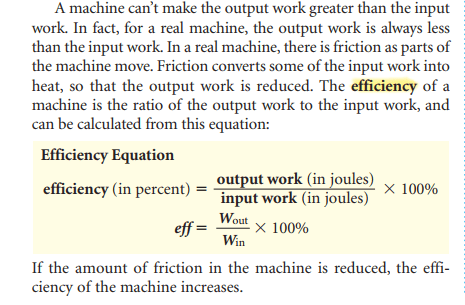
The force that you apply on a machine is the input force. The work you do on the machine is equal to the input force times the distance over which your force is applied. The work that you do on the machine is the input work. Sometimes this force is called the resistance force because the machine is trying to overcome some resistance. The force that the machine applies is the output force. The work that the machine does is the output work.
A simple machine is a machine that does work with only one movement. The six simple machines are the inclined plane, lever, wheel and axle, screw, wedge, and pulley. A machine made up of a combination of simple machines is called a compound machine.
An inclined plane is a flat, sloped surface. Less force is needed to move an object from one height to another using an inclined plane than is needed to lift the object.
An inclined plane is a flat, sloped surface. Less force is needed to move an object from one height to another using an inclined plane than is needed to lift the object.
An inclined plane that moves is called a wedge. A wedge can have one or two sloping sides. The knife is an example of a wedge. An axe and certain types of doorstops are also wedges. Just as for an inclined plane, the mechanical advantage of a wedge increases as it becomes longer and thinner.
A screw is an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder or post. The inclined plane on a screw forms the screw threads. Just like a wedge changes the direction of the effort force applied to it, a screw also changes the direction of the applied force. When you turn a screw, the force applied is changed by the threads to a force that pulls the screw into the material. Friction between the threads and the material holds the screw tightly in place. The mechanical advantage of the screw is the length of the inclined plane
wrapped around the screw divided by the length of the screw.
A lever is any rigid rod or plank that pivots, or rotates, about a point. The point about which the lever pivots is called a fulcrum. A wheel and axle consists of two circular objects of different sizes that are attached in such a way that they rotate together. A pulley consists of a grooved wheel with a rope or cable wrapped over it. A fixed pulley, does not change the force you exert or the distance over which you exert it. Instead, it changes the direction in which you exert your force. A movable pulley, allows you to exert a smaller force to lift the object. More often you will see combinations of fixed and movable
pulleys. Such a combination is called a pulley system. The mechanical advantage of a pulley system is equal to the number of sections of rope pulling up on the object.
prostheses
pivot: axle
peg legs
dragster
aerodynamic
Temperature is a measure of the average value of the kinetic energy of the molecules in random motion. The more kinetic energy the molecules have, the higher the temperature.
Thermometers usually use the expansion and contraction of materials to measure temperature.
The temperature of an object is related to the average kinetic energy of molecules in random motion. But molecules also have potential energy. Potential energy is energy that the molecules have that can be converted into kinetic energy. The sum of the kinetic and potential energy of all the molecules in an object is the thermal energy of the object.
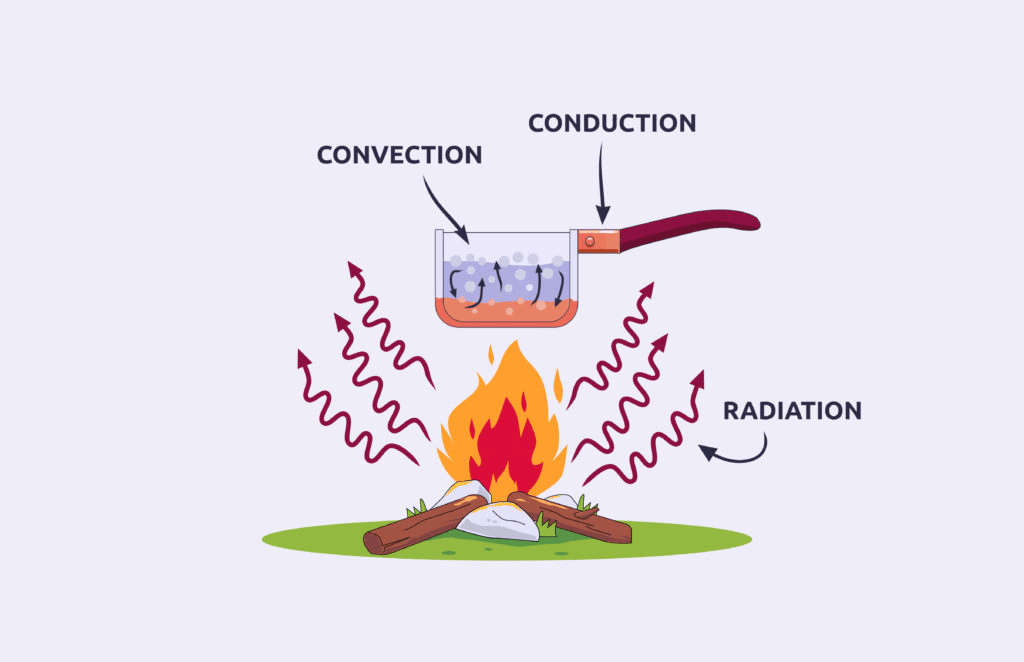
Heat is the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another when the objects are at different temperatures. The amount of thermal energy that is transferred when two objects are brought into contact depends on the difference in temperature between the objects.
Conduction occurs when the particles in a material collide with neighboring particles.
Thermal energy transfer by radiation occurs when energy is transferred by electromagnetic waves.
The transfer of thermal energy by the movement of atoms or molecules from one part of a material to another is called convection.
A conductor is any material that easily transfers thermal energy.
An insulator is a material in which thermal energy doesn’t flow easily.
asphalt: a black, sticky substance, often mixed with small stones or sand, that forms a strong surface when it becomes hard.
The specific heat of a material is the amount of thermal energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the material by 1°C.
Some electric power plants and factories that use water for cooling produce hot water as a by-product. If this hot water is released into an ocean, lake, or river, it will raise the temperature of the water nearby. This increase in the temperature of a body of water caused by adding warmer water is called thermal pollution. Rainwater that is heated after it falls on warm roads or parking lots also can cause thermal pollution if it runs off into a river or lake.
A heat engine is a device that converts thermal energy into mechanical energy. Mechanical energy is the sum of the kinetic and potential energy of an object.
There are other forms of energy besides thermal energy and mechanical energy. For example, chemical energy is energy stored in the chemical bonds between atoms. Radiant energy is the energy carried by electromagnetic waves. Nuclear energy is energy stored in the nuclei of atoms. Electrical energy is the energy carried by electric charges as they move in a circuit.
internal combustion engines
combustion chambers, or cylinders.
crankshaft: a shaft driven by a crank mechanism consisting of a series of cranks and crankpins to which the connecting rods of an engine is attached.
Most cars have an engine with four or more combustion chambers, or cylinders. Usually the more cylinders an engine has, the more power it can produce. Each cylinder contains a piston that can move up and down. A mixture of fuel and air is injected into a combustion chamber and ignited by a spark.When the fuel mixture is ignited, it burns explosively and pushes the piston down. The up-and down motion of the pistons turns a rod called a crankshaft, which turns the wheels of the car.
In internal combustion engines, the fuel burns in a combustion chamber inside the engine.
In diesel engines, the air in the cylinder is compressed to such a high pressure that the highly flammable fuel ignites without the need for a spark plug.
coolant liquid
condenser coil: one of two coils in your air conditioning or heat pump system, in which heat is removed from the refrigerant.
evaporator & condenser
asphalt: a mixture of dark bituminous pitch with sand or gravel, used for surfacing roads, flooring, roofing, etc.
sizzle
crank up
emission
magnetrons
swarm around
static charges
filament
lead: a kind of heavy metal
Unit 7
22
23
24 Wave, sound and light
excerpt
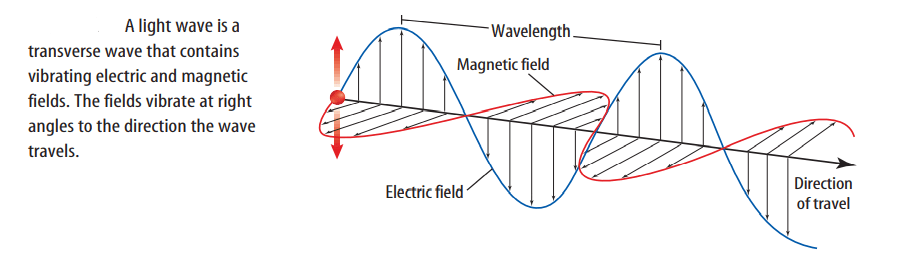
A wave is a disturbance that moves through matter or space. Waves carry energy from one place to another. A transverse wave causes particles in matter to move back and forth at right angles to the
direction in which the wave travels. If you tie a rope to a door handle and shake the end of the rope up and down, transverse waves travel through the rope.
A compressional wave causes particles in matter to move back and forth along the same direction
in which the wave travels.
Seismic waves move through the ground during an earthquake.
perpendicular: at an angle of 90° to a given line, plane, or surface or to the ground.
The distance between one point on a wave and the nearest point moving with the same speed and direction is the wavelength.
The wavelength of a transverse wave is the distance between two adjacent crests or two adjacent troughs.
Frequency of a wave is the number of wave lengths that pass by a point each second.
The amplitude of a transverse wave is half the distance between a crest and trough. As the distance between crests and troughs increases, the amplitude of a transverse wave increases.
The amount of energy that a wave carries past a certain area each second is the intensity of the sound.
Sound with a greater amplitude also has a greater intensity.
The intensity of sound waves is measured in units of decibels (dB).
Loudness is the human perception of the intensity of sound waves. Each increase of 10 dB in intensity multiplies the energy of the sound waves ten times. Most people perceive this as a doubling of the loudness of the sound. An intensity increase of 20 dB corresponds to a hundred times the energy and an increase in loudness of about four times.
Pitch is the human perception of the frequency of sound.
The sounds from a tuba have a low pitch and the sounds from a flute have a high pitch. Sounds with low frequencies have low pitch and sounds with high frequencies have high pitch.
ear canal
funnel
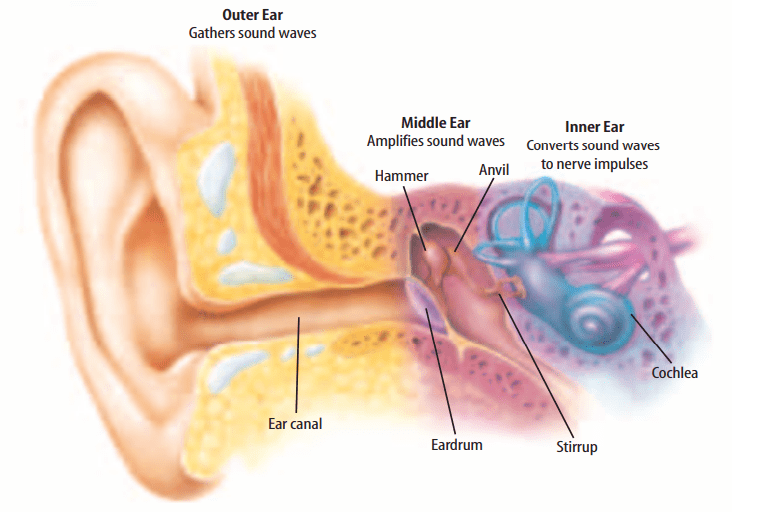
Echoes are sounds that reflect off surfaces. Repeated echoes are called reverberation. Repeated echoes are called reverberation. Concert halls and auditoriums are designed with soft materials on the ceilings and walls to avoid too much reverberation. Theaters like the one in Figure 15 often have curtains on the walls because sounds won’t reflect off soft surfaces. The curtains absorb the energy of the sound waves.
The reflection of sound can be used to locate or identify objects. Echolocation is the process of locating objects by bouncing sounds off them. Bats, dolphins, and other animals emit short, high-frequency sound waves toward a certain area. By interpreting the reflected waves, the animals can locate and determine properties of other animals. Doctors use reflection of sound waves in medicine. Computers can analyze ultrasonic waves that reflect off body parts to produce an internal picture of the body. These pictures help doctors monitor pregnancies, heart problems, and other medical conditions.
Electromagnetic waves are waves that can travel through matter or through empty space.
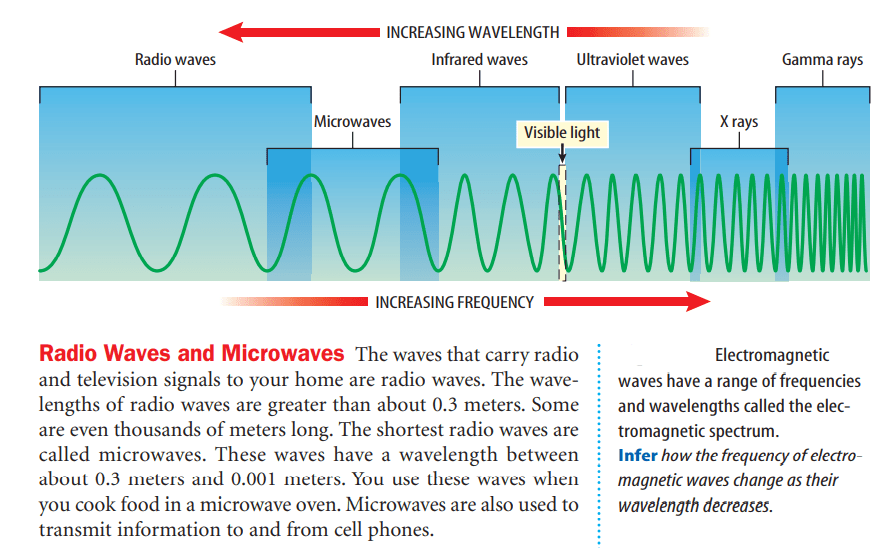
Wavelengths of light are usually expressed in units of nanometers (nm). One nanometer is equal to one billionth of a meter. For example, green light has a wavelength of about 500 nm, or 500 billionths of a meter. A light wave with this wavelength has a frequency of 600 trillion Hz.
The electromagnetic spectrum is the complete range of electromagnetic wave frequencies and wavelengths. At one end of the spectrum the waves have low frequency, long wavelength, and low energy. At the other end of the spectrum the waves have high frequency, short wavelength, and high energy. All of the waves—from radio waves to visible light to gamma rays— are the same kind of waves. They differ from each other only by their frequencies, wavelengths, and energy.
prism
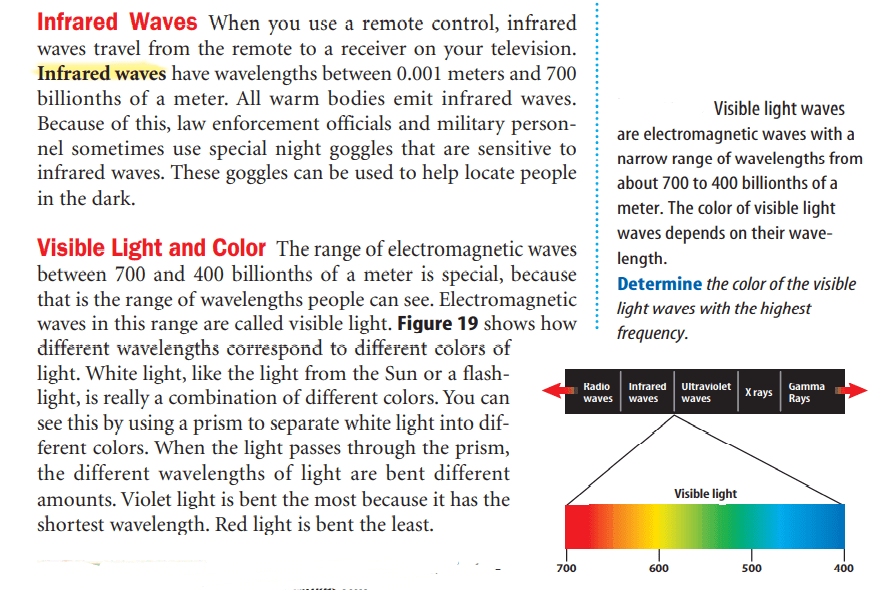

visible spectrum
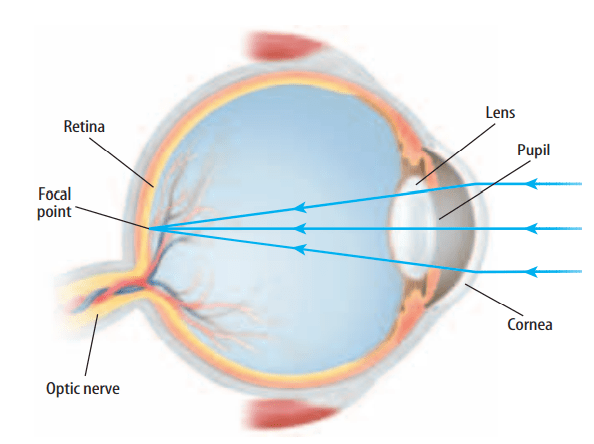
The retina contains over a hundred million light-sensitive cells called rods and cones. Rod cells are sensitive to dim light, and cone cells enable you to see colors. There are three types of cone cells. One type is sensitive to red and yellow light, another type is sensitive to green and yellow light, and the third type is sensitive to blue and violet light. The combination of the signals sent to the brain by all three types of cone cells forms the color image that you see.
quasars and pulsars
drapes

Leave a comment