encounter: unexpectedly experience or be faced with (something difficult or hostile).
spell out: explain
the state of having the right to do or obtain something through satisfaction of the appropriate conditions.
regulation: a rule or directive made and maintained by an authority.
[employ money grants and mandates]
grant: a sum of money given by a government or other organization for a particular purpose.
mandate: an official order or commission to do something.
evolve: develop gradually, especially from a simple to a more complex form.
entity: a thing with distinct and independent existence.
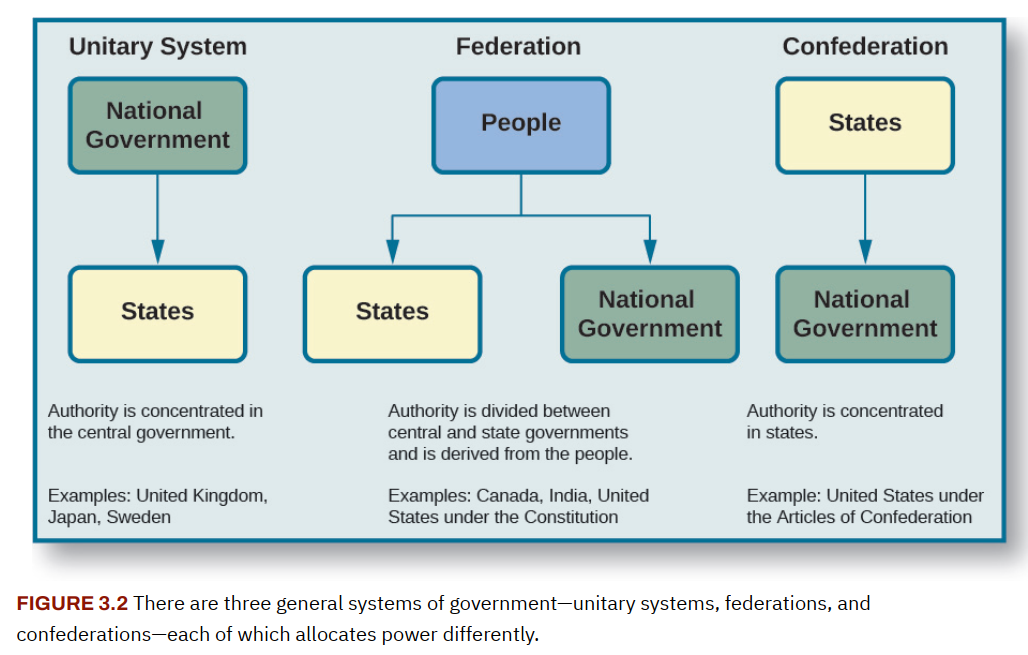
Modern democracies divide governmental power in two general ways; some, like the United States, use a combination of both structures. The first and more common mechanism shares power among three branches of government—the legislature, the executive, and the judiciary. The second, federalism, apportions power between two levels of government: national and subnational. In the United States, the term federal government refers to the government at the national level, while the term states means governments at the subnational level.
Federalism is an institutional arrangement that creates two relatively autonomous levels of government, each possessing the capacity to act directly on behalf of the people with the authority granted to it by the national constitution.
well-being: the state of being comfortable, healthy, or happy.
substantial: of considerable importance, size, or worth.
arduous: involving or requiring strenuous effort; difficult and tiring.
initiative: the ability to assess and initiate things independently.
garner: gather or collect (something, especially information or approval).
bolster: support or strengthen; prop up.
[the involvement of law enforcement agents]
adjudicate: make a formal judgment or decision about a problem or disputed matter.
arbiter: a person who settles a dispute or has ultimate authority in a matter.
regulate: control or maintain the rate or speed of (a machine or process) so that it operates properly.
convey: transport or carry to a place.
A unitary system makes subnational governments dependent on the national government, where significant authority is concentrated. Since then, power has been gradually decentralized through a process of devolution, leading to the creation of regional governments in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland as well as the delegation of specific responsibilities to them.
devolution: the transfer or delegation of power to a lower level, especially by central government to local or regional administration.
delegation: a body of delegates or representatives; a deputation.
The Constitution contains several provisions that direct the functioning of U.S. federalism. Some delineate the scope of national and state power, while others restrict it.
delineate: describe or portray (something) precisely.
enumerate: mention (a number of things) one by one.
integration: the process of combining two or more things into one.
foster: encourage or promote the development of (something, typically something regarded as good).
[elastic clause]
empower: give (someone) the authority or power to do something.
open-ended: having no determined limit or boundary.
consensus: a general agreement.
overlap: extend over so as to cover partly.
Concurrent powers refers to powers which are shared by both the federal government and state governments.
Counterfeiting is a crime, involving the manufacturing or distribution of goods under someone else’s name, and without their permission.
eminent domain: the right of a government or its agent to expropriate private property for public use, with payment of compensation.
impair: weaken or damage something (especially a human faculty or function).
abridge: shorten (a piece of writing) without losing the sense.
immunity: a situation in which you are protected against from legal action.
due process: fair treatment through the normal judicial system, especially as a citizen’s entitlement.
entitlement: the fact of having a right to something.
deprivation: the damaging lack of material benefits considered to be basic necessities in a society.
suspend: temporarily prevent from continuing or being in force or effect.
[writ of habeas corpus]
[bill of attainder] attainder: the forfeiture (lose or giving up) of land and civil rights suffered as a consequence of a sentence of death for treason ( the crime of betraying one’s country) or felony (a crime, typically one involving violence, regarded as more serious than a misdemeanor, and usually punishable by imprisonment for more than one year or by death.).
An ex post facto law is a law that retroactively changes the legal consequences of actions that were committed, or relationships that existed, before the enactment of the law.
retroactively: with effect from a date in the past.
enactment: the process of passing legislation.
Specifically, the government cannot suspend the writ of habeas corpus, which enables someone in custody to petition a judge to determine whether that person’s detention is legal; pass a bill of attainder, a legislative action declaring someone guilty without a trial; or enact an ex post facto law, which criminalizes an act retroactively. The Bill of Rights affirms and expands these constitutional restrictions, ensuring that the government cannot encroach on personal freedoms.
[Supremacy Clause]
prevail: prove more powerful or superior.

Leave a comment