bale of hay
hibernate: (of an animal or plant) spend the winter in a dormant state.
Some may think that a pumpkin is a vegetable, but it is actually a fruit.
rote: mechanical or habitual repetition of something to be learned.
[math counters]
dog pen: a dog shelter.
tile: a thin, flat piece used in Scrabble, mah-jongg, and certain other games.
Navel oranges are a winter orange with thick, bright orange skin and sweet, juicy fruit.
peak season: the time of year when a lot of people travel and prices are usually at their highest.
intervention: a short-term focused teaching programme with objectives aimed at particular students or small groups of students with specific needs.
[intensive intervention]
consolidate: reinforce or strengthen (one’s position or power).
grasp: seize and hold firmly.
legible: (of handwriting or print) clear enough to read.
manipulate: handle or control (a tool, mechanism, etc.), typically in a skillful manner.
syncopated: (of a tune) having a rhythm in which strong notes are not on the beat.
tempo: the speed or pace of a given piece.
brad: (US, elementary school usage) A paper fastener, a fastening device formed of thin, soft metal, such as shim brass, with a round head and a flat, split shank, …
Subitizing is the ability to instantly recognize the number of objects without actually counting them.
inverse: opposite or contrary in position, direction, order, or effect.
pair up
foster: to help (something) grow or develop
align: place or arrange (things) in a straight line.
equivalent: equal in value, amount, function, meaning, etc.
[attend to precision]
shuffle: to move or walk in a sliding dragging manner without lifting the feet.
prerequisite: a thing that is required as a prior condition for something else to happen or exist.
[Have one child model the number with counters.]
kinesthetic: connected with the ability to know where the parts of your body are and how they are moving.
[snip off the wedge]
booth: a stall or stand (as at a fair) for the sale or exhibition of goods
To slant is to tilt or slope sharply to one side.
cardinality: the number of elements in a set or other grouping, as a property of that grouping.
intuitively: without conscious reasoning; instinctively.
discern: perceive or recognize (something).
cumbersome: slow or complicated and therefore inefficient.
wiggle: move or cause to move up and down or from side to side with small rapid movements:
felt: a cloth made of wool and fur often mixed with natural or synthetic fibers through the action of heat, moisture, chemicals, and pressure.
increment: Something added or gained.
[ones]
[tens]
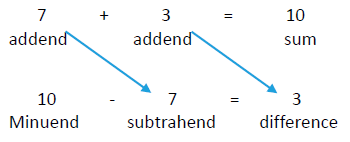
hopscotch
pail
spatial sense
discrediting
vertices: corners
vertex
A square has four straight sides that match.
A square has four sides of equal length. A square has four square vertices.
equilateral triangles
pattern blocks
rhombus
trapezoid
flat surface
curved surface
roll
stack
slide
sphere
cube
cylinder
cone




ahead [][] back
pictograph
initially
pros and cons
linens
a yield sign
crouch down
teensy-weensy
concrete graph
G1
encompass: surround and have or hold within.
The Additive Identity Property states that adding zero to a numer does not change the number: a + 0 = a and 0 + a = a.
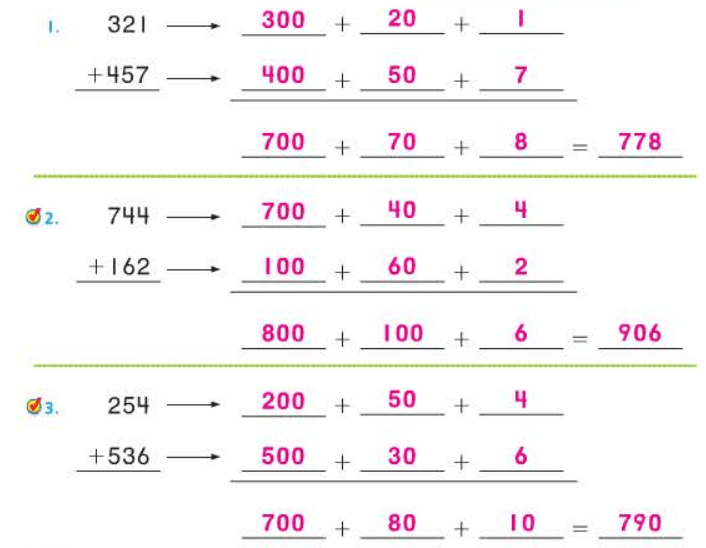
The Commutative Property of Addition states that changing the order of the addends does not change the sum: a + b = b + a.
addition sentence: a number sentence where one number is added to another.
Add 1 + 5 to get 6. If you change the order of the addends, the sum is still 6.
acquisition

number properties
Commutative Property of Addition. the Order Property
hibernate
vertical and horizontal sentences
facilitate
sum – addend = addend
Addition: add to, get together
Subtraction: take apart, take from
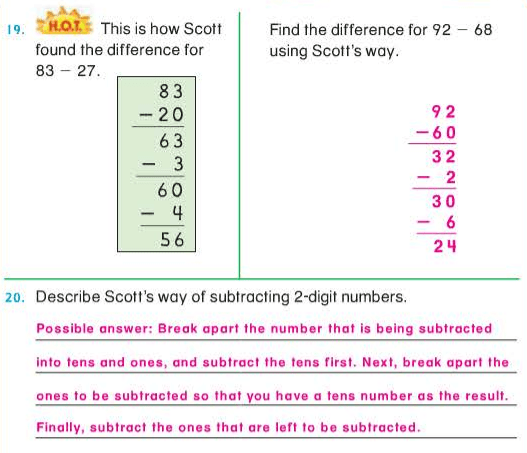
Kate finds a difference of 3 when she solves 9 – 6. She says nine minus six is equal to three.
How many did you start with?
How many did you cross out?
What is the difference?

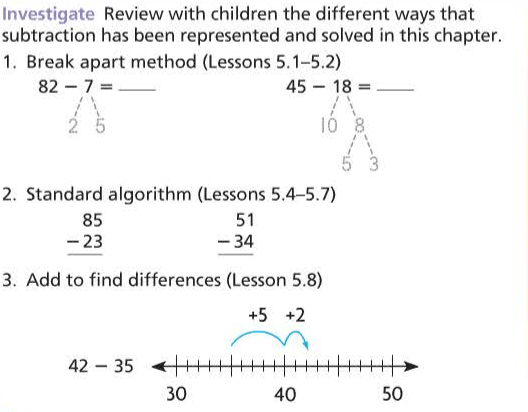
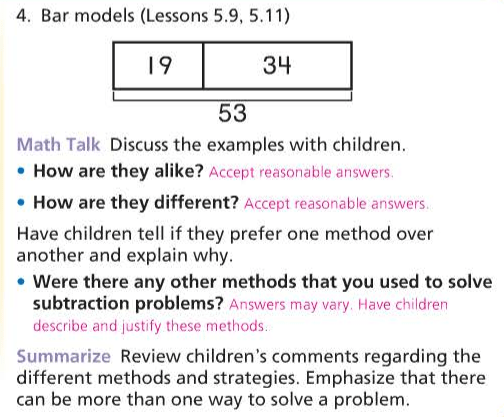
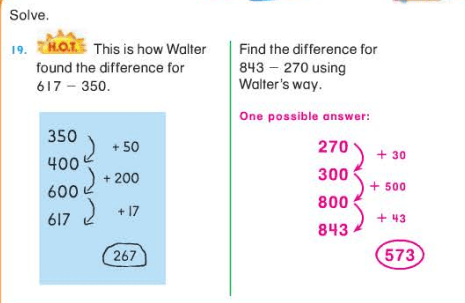
Be mindful of the three different kinds of subtraction problem situations: Take Apart/Addend Unknown, Take from/Start Unknown, and Take from/Change Unknown.
discrete
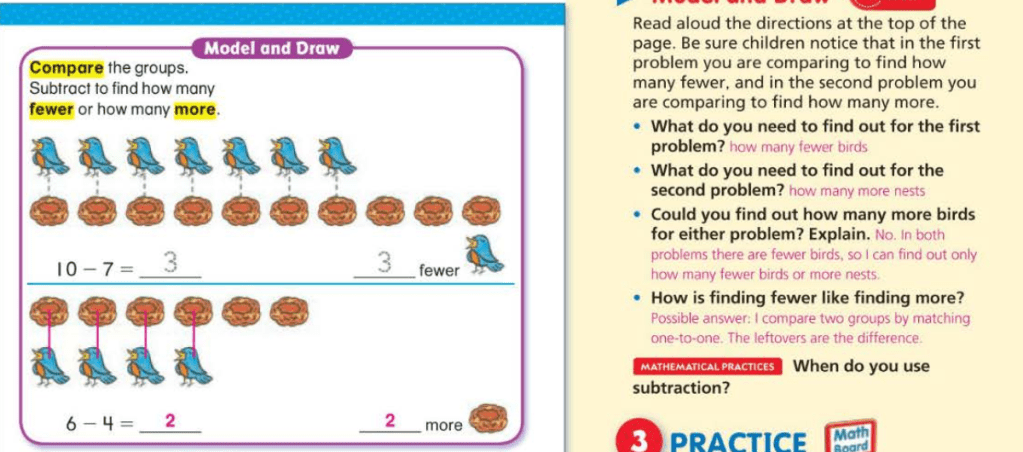
comparing: how many more
Any number subtracted from itself has zerro as the difference.
magnitude
10 is 1 more than 9.
9 – 1 = 8 take apart 9 .
10 – 9 = 1 subtracted 9
9 + 9 = 18 added 9

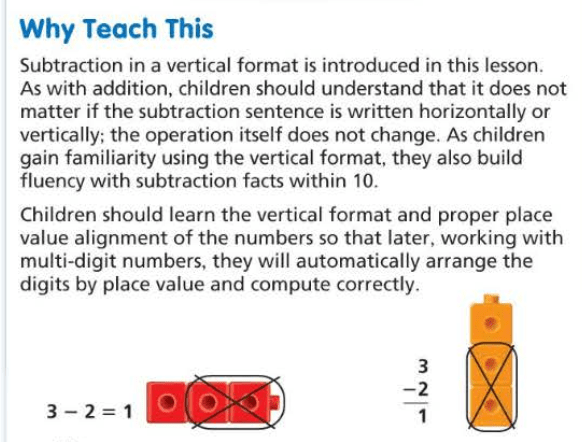
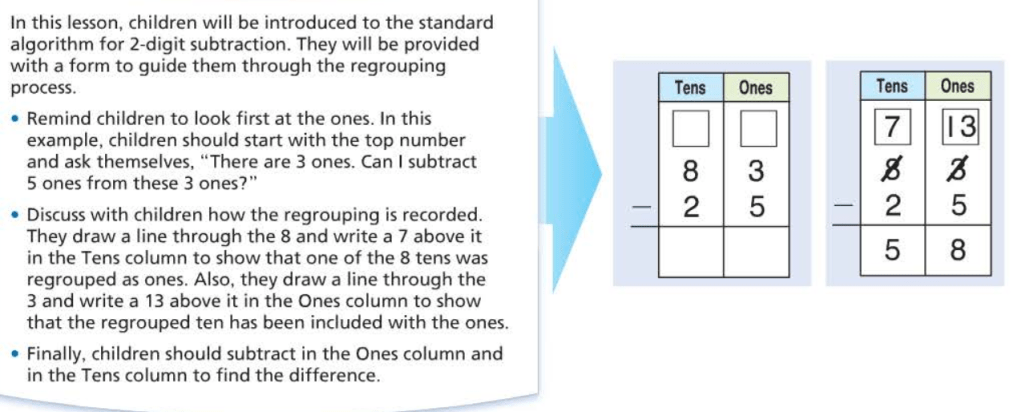
4 – 1 = 3 vertical subtraction sentence. 4 is the starting number (top number), then subtract 1, and 3 is the difference. The line above the 3 means is equal to.
mental math
condensed

addition fact cards
9 + 3 9 count on 3 / count on 3 from 9
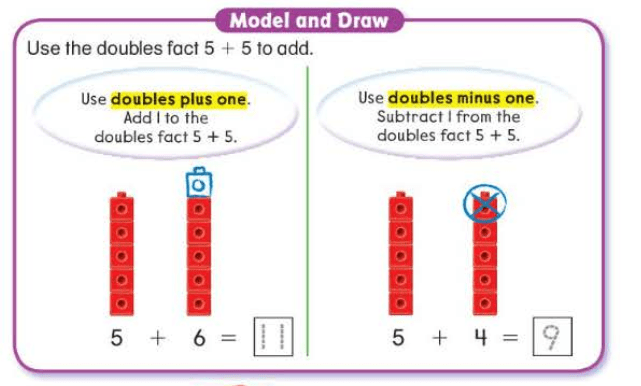
6 + 7 = 6 + 4 + 3 =13 make a ten


The Associative Property rule: a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
perimeter circumference
paper clip
errands
A bar graph: title, labels and numbers.
Three dimensional shapes and there two dimensional flat surfaces
Explain that the dashed lines tell where to fold
Use three-dimensional shapes Trace around the flat surfaces
assemblage
sturdy
G2

count on count back

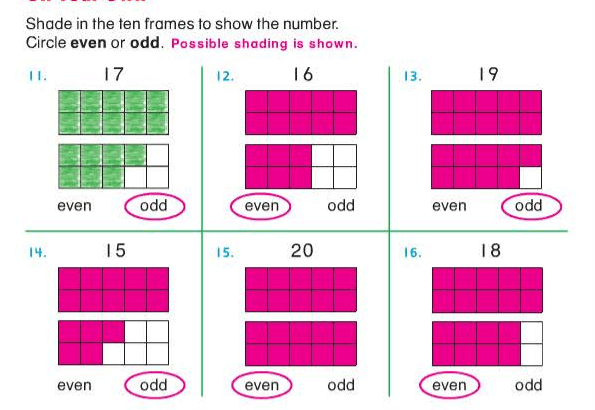
one dot is left over, so it is an odd digit.
a 2-digit number

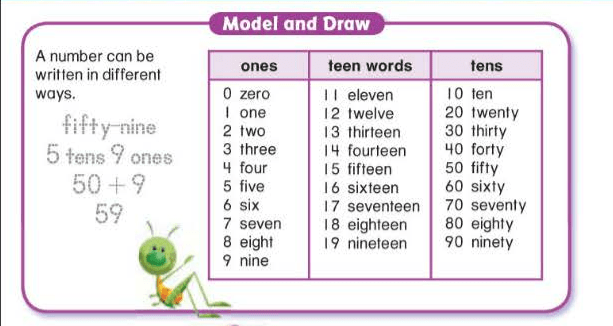
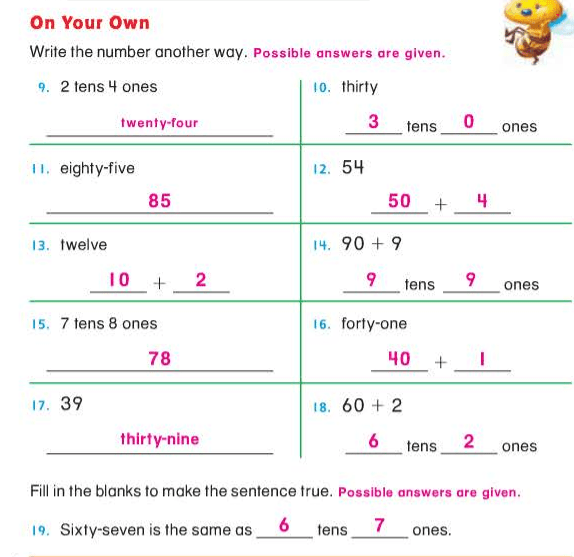
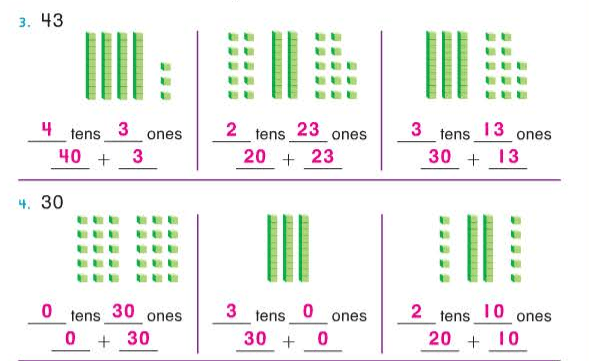
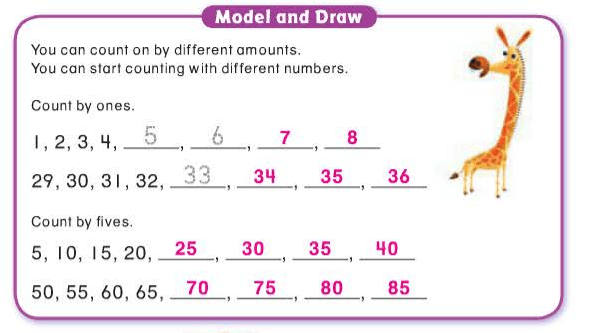
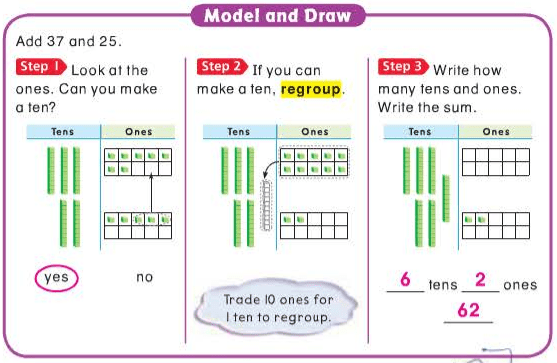
A “-teen” number always has one ten and some ones. A “-ty” number has some tens and a zero in the ones place.
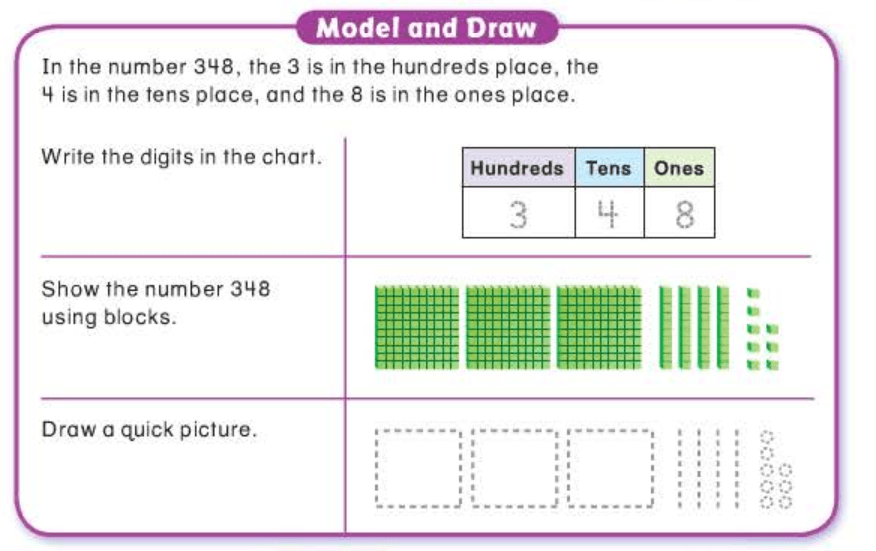

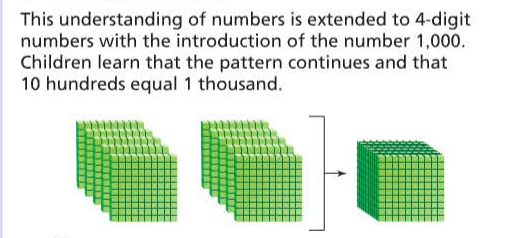
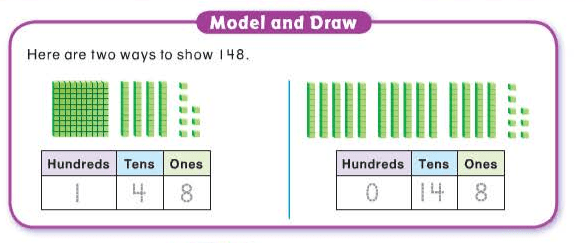




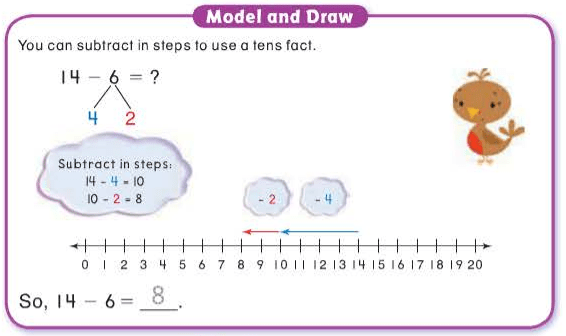

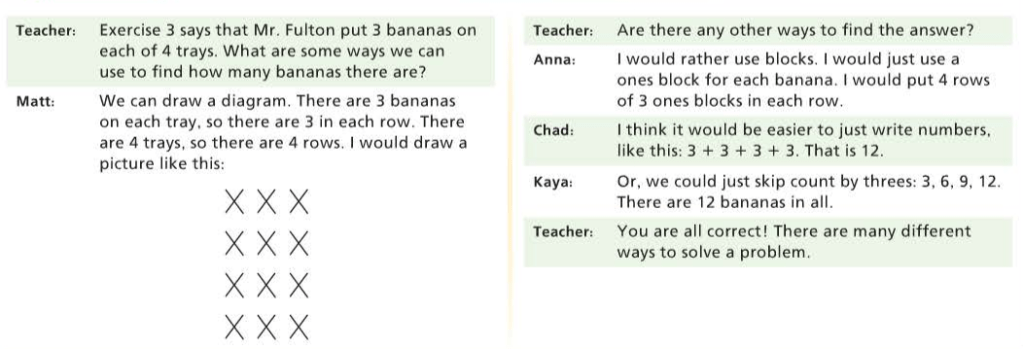
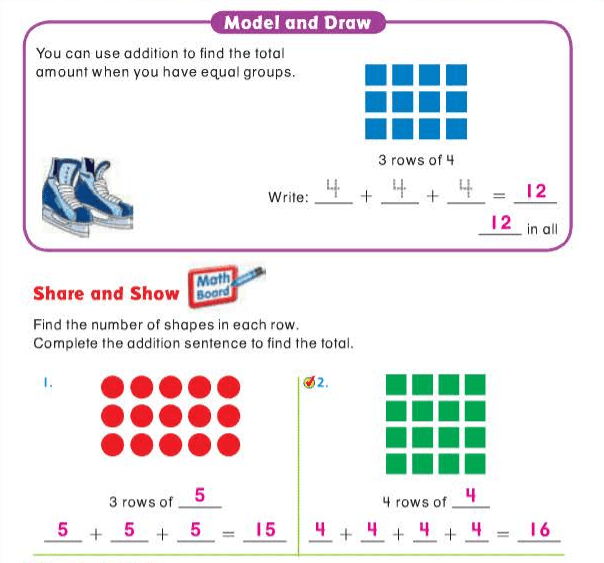

compensation


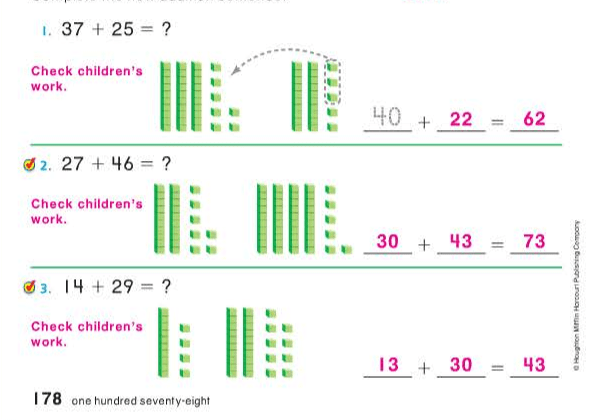




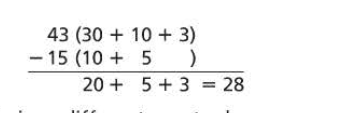

pouch
compartment
vantage
computation
scaffolding: comprises many techniques that allow you to provide extra support to your students.



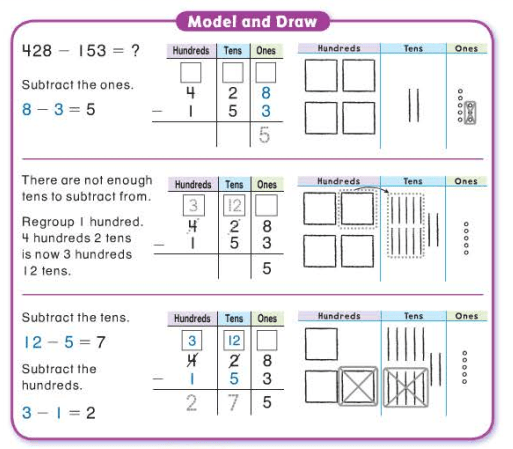


arithmetic
equivalent
analog clock face
measurable attributes
partitioning
Merely writing a number, such as 5, have no meaning as a length if a unit label is not shown.
12 inches is a foot.
masking tape



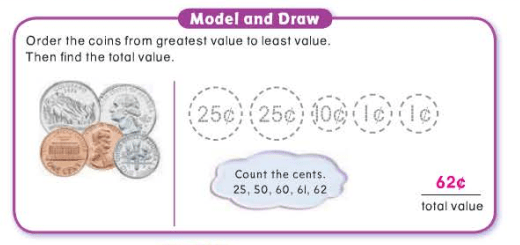


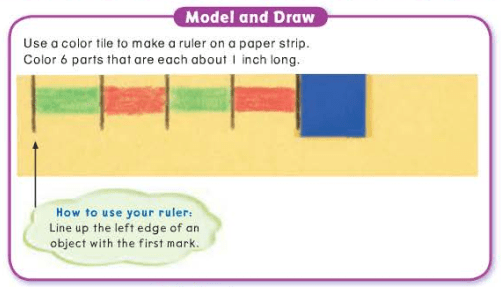
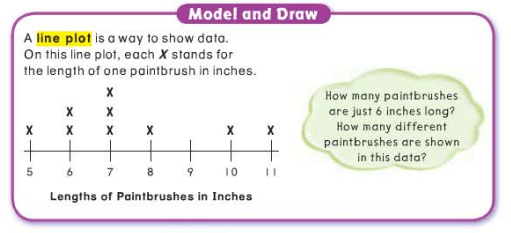


Leave a comment